For ANY series ![]() , we can generate a function
, we can generate a function ![]() such that
such that
Calculus
Lesson
50
Integral
Test and p-series
Back to Dr. Nandor's Calculus Notes Page
Back to Dr. Nandor's Calculus Page
For ANY series
, we can generate a function
such that
![]() . Then, if
. Then, if ![]() , continuous, and decreasing
for all
, continuous, and decreasing
for all ![]() ,
,
then ![]() and
and
![]() either both
converge or both diverge.
either both
converge or both diverge.
Examples: ![]() diverges
and
diverges
and
![]() converges
converges
p-series is the same as the special form that we saw when we did indefinite
integrals.
![]() converges when
converges when ![]() and diverges when
and diverges when ![]()
prove this with the integral test...
when ![]() , it is a special
series called the "harmonic series."
, it is a special
series called the "harmonic series."
We can also show that it diverges like this:
![]()
_____ ___________ _____________
>1/2 >1/2 >1/2
We know this since 2 (1/4s) would = 1/2 so 1/3 and 1/4 is more. 4 (1/8s) would be 1/2, and 1/5 and 1/6 and 1/7 and 1/8 is more, &c.
Practice: For each, determine the convergence:
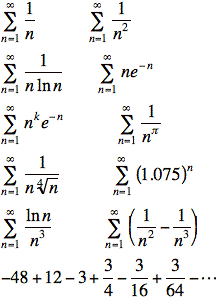
Find the values of p for which ![]() converges.
converges.
Note for integral test: If the first few terms increase and then the
rest of them decrease, take the first few terms out, then
integrate from the earliest term in the new series to infinity.
Example: ![]()