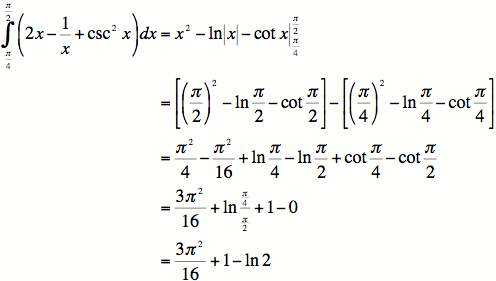Calculus Methods
14 Simple Antiderivatives
Antidifferentiation is, of course, just the opposite of
differentiation!
1A) For polynomials, raise the exponent by one and divide by
the new exponent. The
only exception is ![]() (see next step).
(see next step).
1B)
The antiderivative of
![]() is
is ![]() .
.
1C) For simple trig functions, you must remember the
derivatives. That way, if you see an integral of a trig function
that you already know is the derivative of a simple trig
function, you can just write down the antiderivative. Here is
the list:
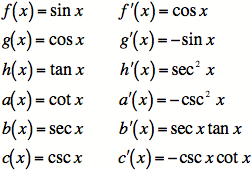
2A) If you are simply looking for the antiderivative, or if you
are evaluating an indefinite integral, don't forget to add C.
2B) If you are evaluating a definite integral, evaluate at the
top limit; then subtract from that what you get when you
evaluate at the bottom limit.
Example
#1: Evaluate ![]() .
.
![]()
Example
#2: Evaluate 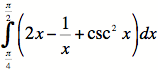 .
.